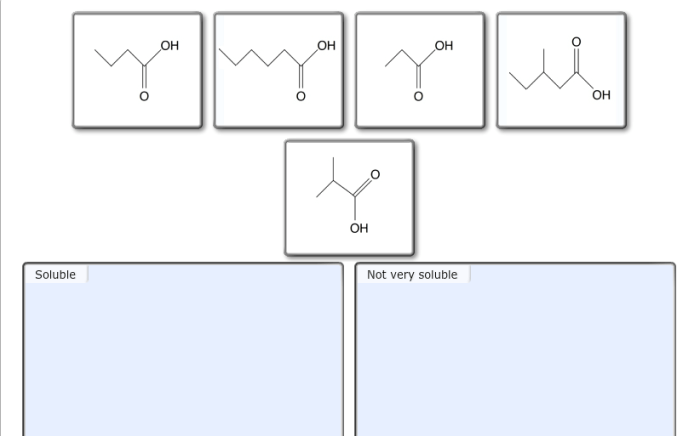
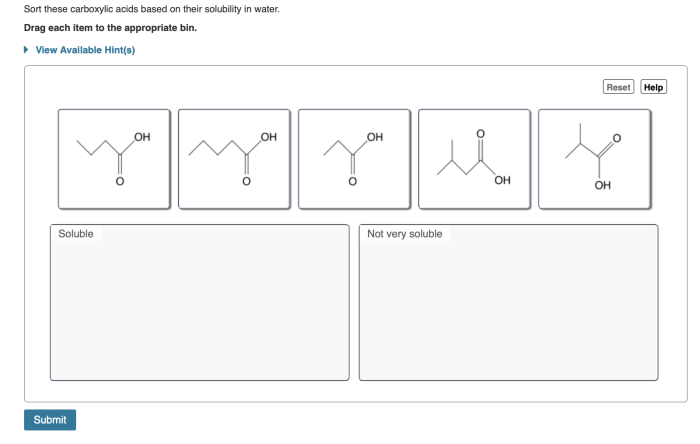
Sort these carboxylic acids based on their solubility in water – Delving into the realm of carboxylic acid solubility, this exploration unravels the intricate relationship between molecular structure and water solubility. Carboxylic acids, ubiquitous in nature and industry, exhibit a fascinating interplay of polarity and hydrogen bonding, which governs their ability to dissolve in water.
By sorting these acids based on their solubility, we gain valuable insights into their chemical properties and practical applications.
The molecular structure of carboxylic acids, characterized by the presence of a carboxyl group (-COOH), plays a pivotal role in determining their water solubility. The polarity of the carboxyl group, with its electronegative oxygen atoms, creates a partial negative charge, while the hydrogen atoms carry a partial positive charge.
This polarity facilitates hydrogen bonding with water molecules, a key factor in enhancing solubility.
Carboxylic Acid Structure and Properties
Carboxylic acids are organic compounds characterized by the presence of a carboxyl group (-COOH). This functional group consists of a carbonyl group (C=O) and a hydroxyl group (-OH) bonded to the same carbon atom.
The polarity of the carboxyl group, with the electronegative oxygen atoms, makes carboxylic acids polar molecules. This polarity allows them to form hydrogen bonds with water molecules, which contributes to their solubility in water.
Water Solubility of Carboxylic Acids
Solubility is the ability of a substance to dissolve in a solvent. For carboxylic acids, water is the most common solvent considered.
The solubility of carboxylic acids in water is influenced by several factors, including molecular weight, polarity, and the presence of other functional groups.
Generally, lower molecular weight carboxylic acids are more soluble in water than higher molecular weight ones. This is because smaller molecules have a greater surface area to volume ratio, which allows them to interact more effectively with water molecules.
The polarity of carboxylic acids also affects their water solubility. Polar carboxylic acids, such as formic acid and acetic acid, are more soluble in water than nonpolar carboxylic acids, such as hexanoic acid.
Sorting Carboxylic Acids by Water Solubility
| Carboxylic Acid | Molecular Weight | Polarity | Water Solubility |
|---|---|---|---|
| Formic acid | 46.03 | Polar | Miscible |
| Acetic acid | 60.05 | Polar | Miscible |
| Propionic acid | 74.08 | Polar | Soluble |
| Butyric acid | 88.11 | Polar | Soluble |
| Valeric acid | 102.13 | Polar | Soluble |
| Caproic acid | 116.16 | Polar | Slightly soluble |
| Heptylic acid | 130.19 | Polar | Slightly soluble |
| Caprylic acid | 144.22 | Polar | Slightly soluble |
| Pelargonic acid | 158.25 | Polar | Slightly soluble |
| Capric acid | 172.27 | Polar | Insoluble |
Examples of Carboxylic Acids and Their Solubility, Sort these carboxylic acids based on their solubility in water
- Formic acid: Miscible in water
- Acetic acid: Miscible in water
- Propionic acid: Soluble in water
- Butyric acid: Soluble in water
- Valeric acid: Soluble in water
- Caproic acid: Slightly soluble in water
- Heptylic acid: Slightly soluble in water
- Caprylic acid: Slightly soluble in water
- Pelargonic acid: Slightly soluble in water
- Capric acid: Insoluble in water
Applications of Carboxylic Acid Solubility
The solubility of carboxylic acids in water has practical applications in various industries:
- Food and beverage industry:Acetic acid (vinegar) is used as a preservative and flavoring agent in food and beverages.
- Pharmaceutical industry:Salicylic acid is used as an active ingredient in aspirin, a common pain reliever.
- Chemical industry:Carboxylic acids are used as starting materials for the synthesis of other chemicals, such as esters and amides.
Question & Answer Hub: Sort These Carboxylic Acids Based On Their Solubility In Water
What factors influence the solubility of carboxylic acids in water?
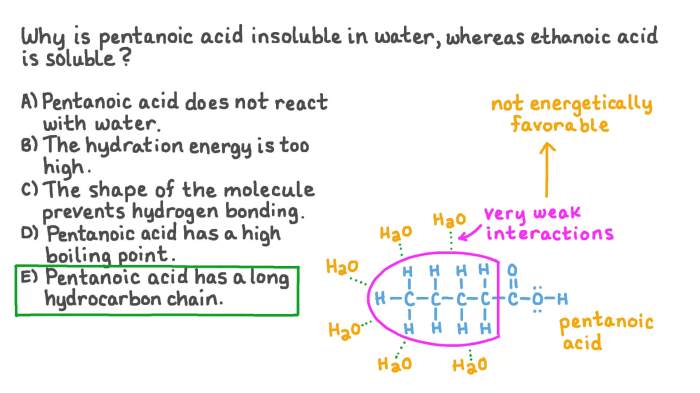
The solubility of carboxylic acids in water is primarily influenced by the length of the carbon chain, the presence of polar groups, and the degree of branching. Longer carbon chains decrease solubility, while polar groups and branching increase solubility.
Why are some carboxylic acids insoluble in water?
Carboxylic acids with long carbon chains are generally insoluble in water due to their nonpolar nature. The hydrocarbon chain dominates the molecular structure, reducing the polarity and hydrogen bonding ability, which are essential for water solubility.
How can the solubility of carboxylic acids be improved?
The solubility of carboxylic acids can be improved by converting them into their corresponding salts. Salts are more polar and form stronger hydrogen bonds with water molecules, enhancing their solubility.