Classify 1 and 2 using all relationships that apply is a fundamental concept in various domains, providing a systematic approach to organizing and understanding complex data. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of relationships and classification, empowering readers to effectively categorize items and make informed decisions.
Relationships between items can be diverse, ranging from hierarchical to associative, and understanding these relationships is crucial for accurate classification. By utilizing multiple relationships, we can achieve a more nuanced and accurate understanding of the data at hand.
Relationships and Classification
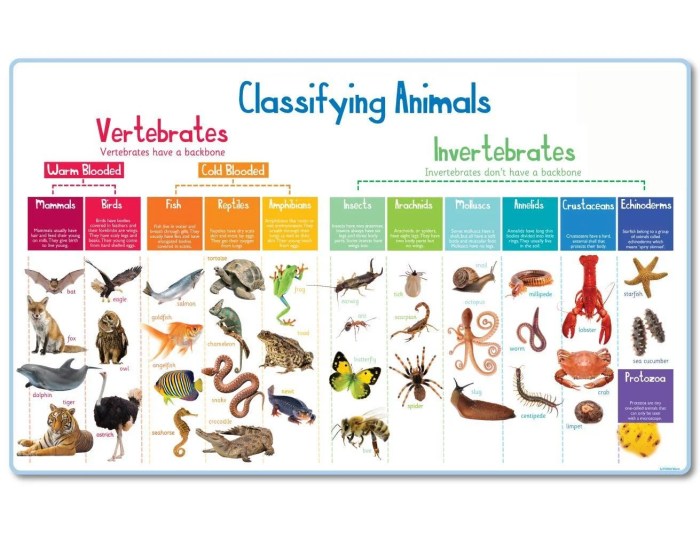
In the realm of data organization and analysis, relationships and classification play a crucial role in structuring and interpreting information. Relationships establish connections between items, while classification organizes these items into meaningful categories based on their shared characteristics.
Types of Relationships
- One-to-One:A relationship where each item in one set is associated with exactly one item in another set.
- One-to-Many:A relationship where each item in one set is associated with multiple items in another set.
- Many-to-Many:A relationship where each item in one set can be associated with multiple items in another set, and vice versa.
Concept of Classification
Classification involves organizing items into groups based on their similarities and differences. It helps to impose structure on data, making it easier to understand and analyze. Classification criteria can include physical attributes, behavioral patterns, or any other relevant characteristics.
Examples of Classification Using Relationships
- Classifying animals into species based on their genetic relationships.
- Categorizing customers into segments based on their purchase history.
- Organizing documents into folders based on their content.
Classifying Items Using Relationships
To classify items using relationships, follow these steps:
Steps Involved
- Identify Relevant Relationships:Determine the relationships that are meaningful for the classification task.
- Establish Classification Criteria:Define the criteria that will be used to group the items into categories.
- Apply Relationships:Use the identified relationships to assign items to appropriate categories based on their shared characteristics.
- Validate Classification:Verify the accuracy and consistency of the classification by examining the results and making any necessary adjustments.
Importance of Multiple Relationships
Using multiple relationships for classification enhances accuracy by considering various aspects of the items. It reduces the likelihood of misclassification due to relying on a single relationship.
Example: Classifying Items into Two Categories
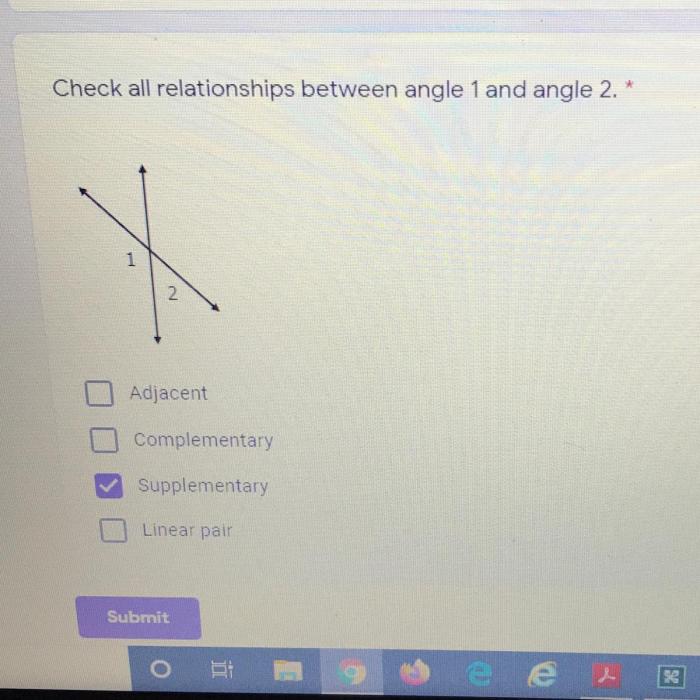
Scenario:Classify a set of products into “Electronic Devices” and “Household Appliances”.
Reasoning Behind Classification, Classify 1 and 2 using all relationships that apply
The following relationships were used to classify the products:
- Power Source:Electronic devices use electricity, while household appliances can use gas or electricity.
- Function:Electronic devices are primarily used for communication, entertainment, or information processing, while household appliances perform specific tasks related to household maintenance.
Implications of Classification
The classification has implications for product placement, marketing strategies, and inventory management. It helps retailers organize their products efficiently and target the right customer segments for each category.
Tools and Techniques for Classification: Classify 1 And 2 Using All Relationships That Apply
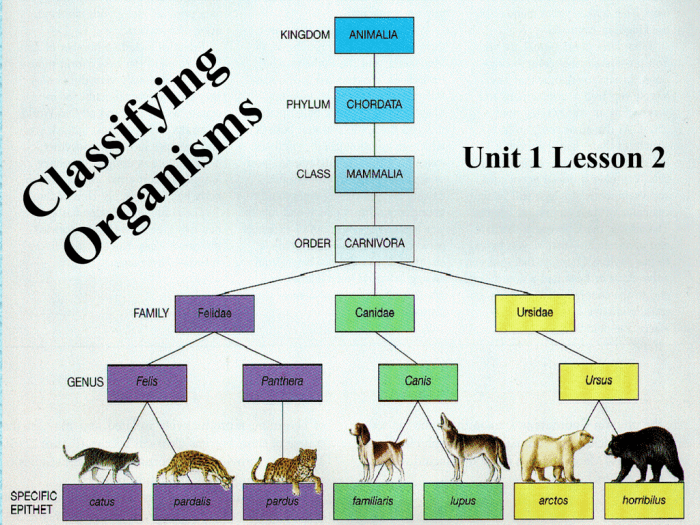
Various tools and techniques can assist in the classification process:
Tools and Techniques
- Decision Trees:Hierarchical structures that use a series of rules to classify items.
- Cluster Analysis:Groups similar items into clusters based on their characteristics.
- Support Vector Machines:Classifies items by creating boundaries between different categories.
- Machine Learning Algorithms:Uses training data to learn classification rules.
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Tool | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Decision Trees | Easy to interpret, fast | Can be biased, not suitable for complex data |
| Cluster Analysis | Identifies natural groupings, handles missing data | Can be computationally expensive, sensitive to parameter settings |
| Support Vector Machines | Handles high-dimensional data, good for binary classification | Can be computationally expensive, requires careful parameter tuning |
| Machine Learning Algorithms | Can learn complex relationships, handles large datasets | Requires training data, can be difficult to interpret |
Selecting the Right Tool
The choice of tool depends on the nature of the data, the desired level of accuracy, and the computational resources available.
Question Bank
What is the significance of using multiple relationships for classification?
Utilizing multiple relationships provides a more comprehensive understanding of the data, as it considers the various connections and dependencies between items. This leads to more accurate and nuanced classification outcomes.
How can I identify the relevant relationships for classification?
Identifying relevant relationships requires careful analysis of the data and understanding the context of the classification task. Domain knowledge and expert insights can be invaluable in determining the most appropriate relationships to use.
What are some common tools and techniques used for classification?
Various tools and techniques are available for classification, including decision trees, clustering algorithms, and machine learning models. The choice of tool or technique depends on the nature of the data, the classification task, and the desired level of accuracy.