Identify the epimer of d-allose at c-2 c-3 and c-4 – Embark on a scientific journey to identify the epimers of D-allose at C-2, C-3, and C-4. This exploration delves into the intricacies of carbohydrate chemistry, unveiling the structural nuances that distinguish these closely related molecules.
Epimers, isomers that differ in the configuration of a single chiral center, play a crucial role in biological systems. Understanding their properties and nomenclature is essential for comprehending their diverse functions in nature.
Epimers of D-Allose
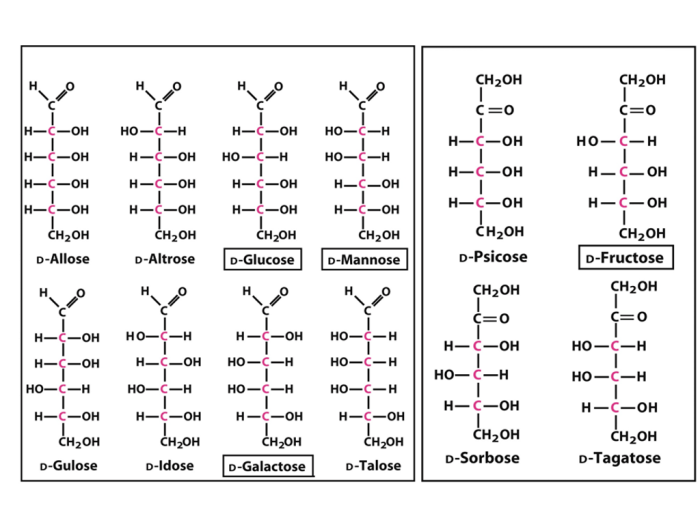
Epimers are stereoisomers that differ in the configuration at a single stereogenic center. D-Allose is a hexose sugar with four stereogenic centers. This article will identify and discuss the epimers of D-allose at C-2, C-3, and C-4.
Epimers at C-2
The epimer of D-allose at C-2 is D-altrose. These two sugars differ in the configuration at C-2, with D-allose having an OH group pointing down and D-altrose having an OH group pointing up.
Epimers at C-3
The epimer of D-allose at C-3 is D-glucose. These two sugars differ in the configuration at C-3, with D-allose having an OH group pointing down and D-glucose having an OH group pointing up.
Epimers at C-4
The epimer of D-allose at C-4 is D-mannose. These two sugars differ in the configuration at C-4, with D-allose having an OH group pointing down and D-mannose having an OH group pointing up.
Comparison of Epimers
The following table compares the structures of D-allose and its epimers at C-2, C-3, and C-4.
| Sugar | C-2 | C-3 | C-4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| D-Allose | OH down | OH down | OH down |
| D-Altrose | OH up | OH down | OH down |
| D-Glucose | OH down | OH up | OH down |
| D-Mannose | OH down | OH down | OH up |
As can be seen from the table, the epimers of D-allose differ only in the configuration at the specified carbon atom. All other stereogenic centers have the same configuration.
Nomenclature of Epimers, Identify the epimer of d-allose at c-2 c-3 and c-4
The systematic nomenclature rules for naming epimers involve using the prefix “epi-” followed by the name of the parent sugar and the number of the stereogenic center that is different. For example, D-altrose is named as “epi-D-allose” because it is an epimer of D-allose at C-2.
Question & Answer Hub: Identify The Epimer Of D-allose At C-2 C-3 And C-4
What is the difference between an epimer and an enantiomer?
Epimers are stereoisomers that differ in the configuration of a single chiral center, while enantiomers are stereoisomers that are mirror images of each other.
How are epimers named?
Epimers are named using the prefixes “epi” or “allo” to indicate the inverted configuration at the specific chiral center.
What are the biological implications of epimers?
Epimers can have different biological activities and functions due to their distinct structural and chemical properties.