Gravel is being dumped from a conveyor belt, a process that plays a crucial role in various industries and applications. This article delves into the intricacies of gravel dumping, exploring its multifaceted aspects, from the technicalities of the process to its environmental implications and economic considerations.
The intricate process of gravel dumping involves a sequence of steps, employing specialized equipment and adhering to stringent safety regulations. Understanding these steps is essential for efficient and responsible gravel management.
Gravel Dumping Process

Gravel dumping from a conveyor belt involves a systematic process to efficiently discharge and distribute gravel for various applications. The process typically encompasses the following steps:
Equipment and Machinery, Gravel is being dumped from a conveyor belt
- Conveyor belt: A motorized belt system that transports gravel from a source to the discharge point.
- Hopper: A receiving bin that collects gravel from the conveyor belt and controls its flow rate.
- Dump truck or receiving vessel: A vehicle or container that receives the gravel from the hopper.
- Support equipment: Bulldozers, graders, and compactors may be used to spread and level the gravel.
Safety Precautions and Regulations
Gravel dumping operations require adherence to safety protocols and regulations to minimize risks. These may include:
- Proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE), such as hard hats, safety glasses, and gloves.
- Adequate signage and barriers to prevent unauthorized access to the dumping area.
- Regular inspection and maintenance of equipment to ensure safe operation.
- Compliance with environmental regulations to minimize dust, noise, and potential contamination.
- Road and highway construction: Gravel serves as a base layer or sub-base for road surfaces.
- Building foundations: Gravel is used to provide a stable and well-drained base for structures.
- Drainage systems: Gravel is utilized in drainage trenches and French drains to facilitate water flow.
- Garden paths and walkways: Gravel creates a durable and aesthetically pleasing surface for outdoor areas.
- Decorative landscaping: Gravel is used as a decorative element in gardens and around water features.
- Erosion control: Gravel can help stabilize slopes and prevent erosion in landscaping projects.
- Agriculture: Gravel is used as a soil amendment to improve drainage and soil structure.
- Water filtration: Gravel is employed in water filtration systems to remove impurities.
- Industrial processes: Gravel is utilized as a raw material in various industrial processes, such as glass and concrete production.
- Proper site selection to minimize erosion and sedimentation.
- Dust suppression measures, such as water spraying or dust collectors.
- Noise barriers and mufflers to reduce noise pollution.
- Regular monitoring and maintenance to ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
- Increased use of renewable energy sources to power equipment.
- Integration of artificial intelligence (AI) for predictive maintenance and process optimization.
- Development of sustainable gravel alternatives to reduce environmental impact.
Applications and Uses
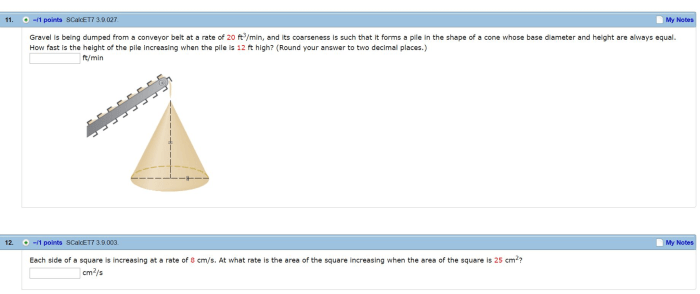
Gravel dumping from a conveyor belt finds applications in a wide range of industries and projects, including:
Construction
Landscaping
Other Applications
Impact on the Environment

Gravel dumping can potentially impact the environment if not managed responsibly. Potential concerns include:
Erosion and Sedimentation
Improper dumping or excessive amounts of gravel can lead to erosion and sedimentation, which can damage water bodies and aquatic ecosystems.
Dust and Air Pollution
Gravel dumping operations can generate dust, which can contribute to air pollution and respiratory issues.
Noise Pollution
The machinery and vehicles involved in gravel dumping can produce significant noise, potentially affecting nearby communities.
Mitigating Impacts
To mitigate these impacts, it is crucial to implement best practices, such as:
Economic Considerations
Gravel dumping operations involve various economic factors that influence their profitability:
Equipment and Labor Costs
The cost of equipment, including the conveyor belt, hopper, and dump trucks, can be significant.
Material Costs
The cost of gravel itself, as well as its transportation to the dumping site, needs to be considered.
Labor Costs
The number of workers required for the operation and their wages impact the overall labor costs.
Return on Investment
The return on investment for gravel dumping operations depends on factors such as the scale of the project, the demand for gravel, and the efficiency of the operation.
Innovations and Advancements
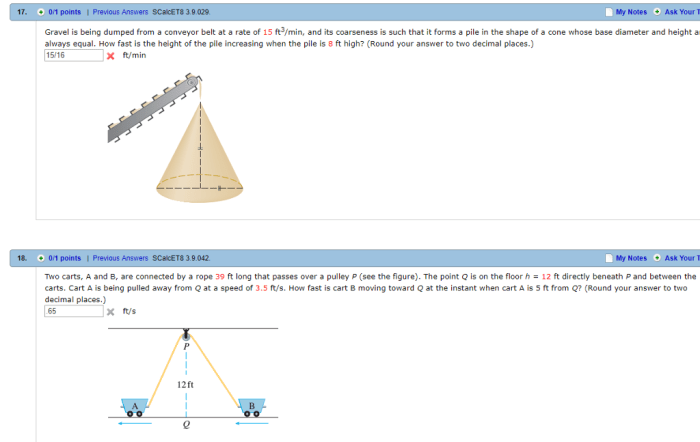
Technological advancements have led to innovations in gravel dumping:
Automated Systems
Automated conveyor systems and dump trucks can improve efficiency and reduce labor costs.
GPS Tracking and Monitoring
GPS tracking systems allow for real-time monitoring of equipment and materials, optimizing the operation.
Dust Suppression Technologies
Advanced dust suppression systems, such as water misting or electrostatic precipitators, minimize dust emissions.
Future Trends
Future developments in gravel dumping technology may include:
Clarifying Questions: Gravel Is Being Dumped From A Conveyor Belt
What are the key safety precautions to consider during gravel dumping?
Safety precautions include wearing appropriate protective gear, maintaining a safe distance from the dumping area, and ensuring proper signage and barriers to prevent accidents.
How can we minimize the environmental impact of gravel dumping?
Minimizing environmental impact involves selecting appropriate dumping sites, implementing erosion control measures, and adhering to regulations to prevent water and soil contamination.
What are the economic benefits of gravel dumping?
Gravel dumping can reduce transportation costs, improve project efficiency, and provide a cost-effective solution for waste management in certain industries.