Imperialism in Africa Worksheet Answer Key provides a comprehensive guide to understanding the profound impact of European colonialism on the African continent. This engaging resource offers detailed answers to questions exploring the political, economic, social, and cultural consequences of imperialism, illuminating the complexities of this transformative period.
Through a historical overview, analysis of methods and effects, and examination of resistance movements and decolonization, this worksheet unravels the intricate web of imperialism, its motivations, and its lasting legacy on African societies and economies.
Imperialism in Africa
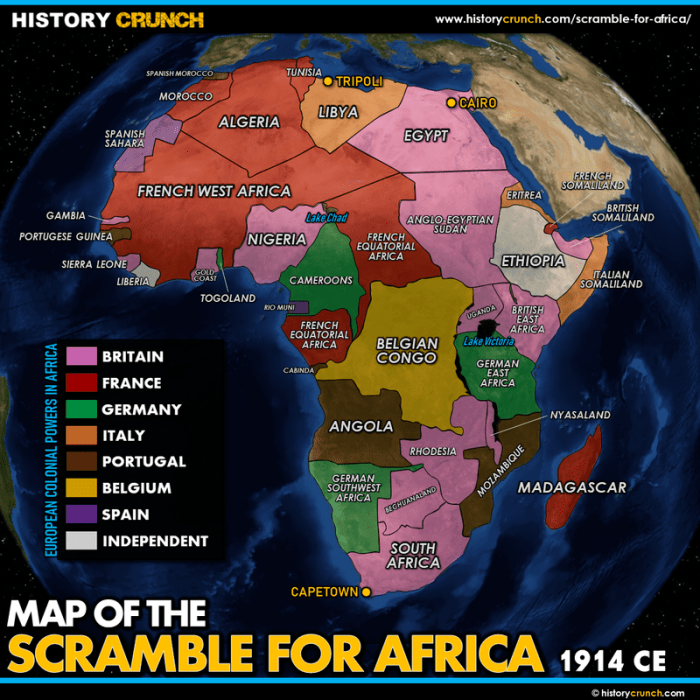
Imperialism is a policy or practice by which a country increases its power and wealth by acquiring and maintaining colonies in other countries. European imperialism in Africa began in the late 19th century and lasted until the mid-20th century.
Methods and Effects of Imperialist Rule
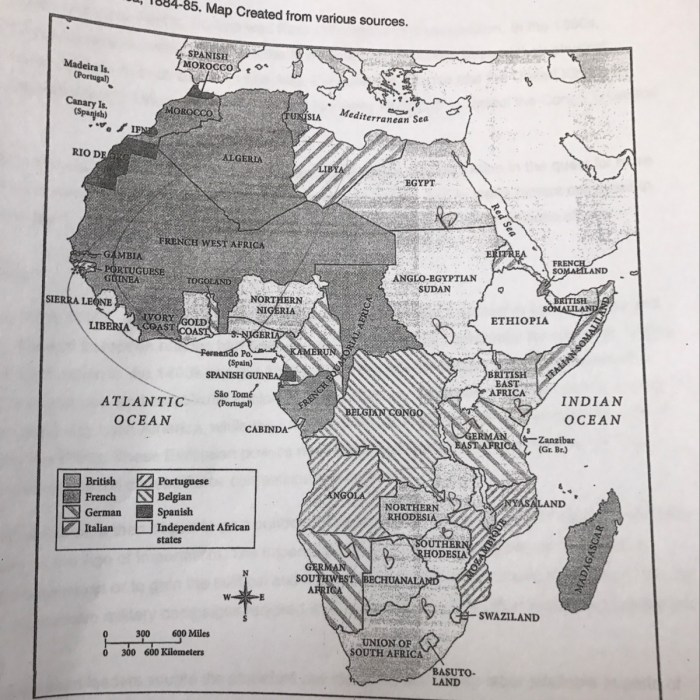
European powers used a variety of political, economic, and social methods to control Africa. They established colonial governments, imposed taxes, and forced Africans to work on plantations and mines. Imperialism had a profound impact on African societies, leading to cultural, economic, and political changes.
Political Effects
- European powers established colonial governments that were often authoritarian and repressive.
- Africans were denied basic rights and freedoms.
- Traditional African political systems were undermined.
Economic Effects
- European powers exploited African resources, such as minerals, agricultural products, and labor.
- This led to the development of a cash crop economy in Africa.
- African economies became dependent on European markets.
Social Effects
- Imperialism led to the introduction of Western education, religion, and values into African societies.
- This had a profound impact on African cultures.
- New social classes and identities emerged in response to imperialism.
Economic Exploitation and Resource Extraction
European powers exploited African resources in a variety of ways. They forced Africans to work on plantations and mines, and they also seized African land and resources.
Resource Extraction, Imperialism in africa worksheet answer key
- European powers extracted a wide range of resources from Africa, including minerals, agricultural products, and timber.
- This led to the development of a cash crop economy in Africa.
- African economies became dependent on European markets.
Impact on African Economies
- Resource extraction had a negative impact on African economies.
- It led to the loss of traditional African industries.
- It also led to the exploitation of African workers.
Social and Cultural Transformation: Imperialism In Africa Worksheet Answer Key

Imperialism had a profound impact on African societies and cultures. It led to the introduction of Western education, religion, and values into African societies.
Western Education
- European powers established schools in Africa to educate Africans in Western culture and values.
- This led to the development of a new African elite that was educated in Western ways.
- The introduction of Western education also led to the decline of traditional African education systems.
Western Religion
- European missionaries spread Christianity throughout Africa.
- This led to the conversion of many Africans to Christianity.
- The introduction of Western religion also led to the decline of traditional African religions.
Western Values
- European powers introduced Western values into African societies, such as individualism and materialism.
- This led to the erosion of traditional African values.
- The introduction of Western values also led to the development of new social classes and identities in Africa.
Decolonization and Its Legacy
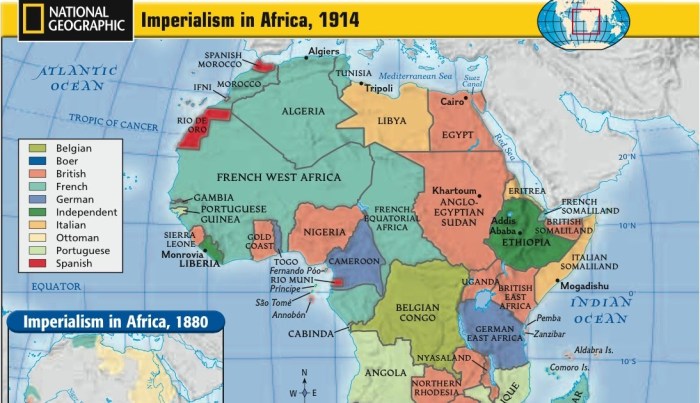
Decolonization is the process by which African countries gained independence from European powers. It began in the mid-20th century and lasted until the early 1960s.
Factors Leading to Decolonization
- The rise of nationalism in Africa.
- The weakening of European powers after World War II.
- The Cold War.
Process of Independence
- African countries gained independence through a variety of means, including negotiation, violence, and revolution.
- The process of independence was often difficult and protracted.
- Many African countries faced challenges after independence, such as economic instability, political instability, and ethnic conflict.
Legacy of Imperialism
- Imperialism had a lasting impact on African societies and economies.
- It led to the creation of new borders and the division of African peoples.
- It also led to the exploitation of African resources and the underdevelopment of African economies.
Clarifying Questions
What were the primary motivations for European imperialism in Africa?
Economic gain, political power, and the desire to spread Western civilization were key drivers of European imperialism in Africa.
How did imperialism impact African societies?
Imperialism brought about significant cultural, economic, and political changes in African societies, including the introduction of Western education, religion, and values, as well as the exploitation of resources and labor.
What were the major resistance movements against imperialism in Africa?
Resistance to imperialism took various forms, including armed revolts, boycotts, and nonviolent protests, led by nationalist leaders and movements.