Delve into the realm of field level auditing in Pega, where meticulous examination empowers organizations to elevate their operations and optimize performance. This comprehensive guide unveils the intricacies of this essential practice, providing a roadmap to unlock its full potential.
As we navigate the nuances of field level auditing, we’ll explore its methods, data collection techniques, reporting strategies, and best practices. Join us on this enlightening journey to transform your auditing endeavors and propel your organization towards excellence.
Field Level Auditing Overview
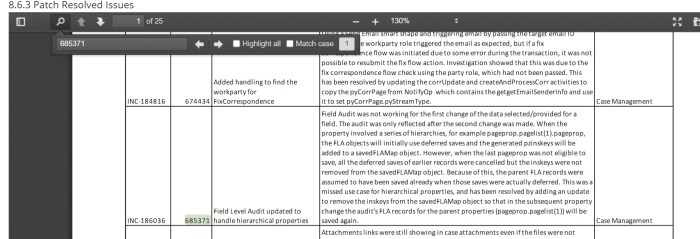
Field level auditing in Pega is a powerful tool that allows auditors to track changes made to individual fields within a case. This can be extremely valuable for ensuring the integrity of data and identifying any potential fraud or errors.
There are many benefits to using field level auditing in Pega, including:
- Increased data integrity
- Improved fraud detection
- Reduced errors
- Enhanced compliance
However, there are also some challenges to using field level auditing in Pega, including:
- Increased storage requirements
- Performance overhead
- Complexity
Methods and Procedures
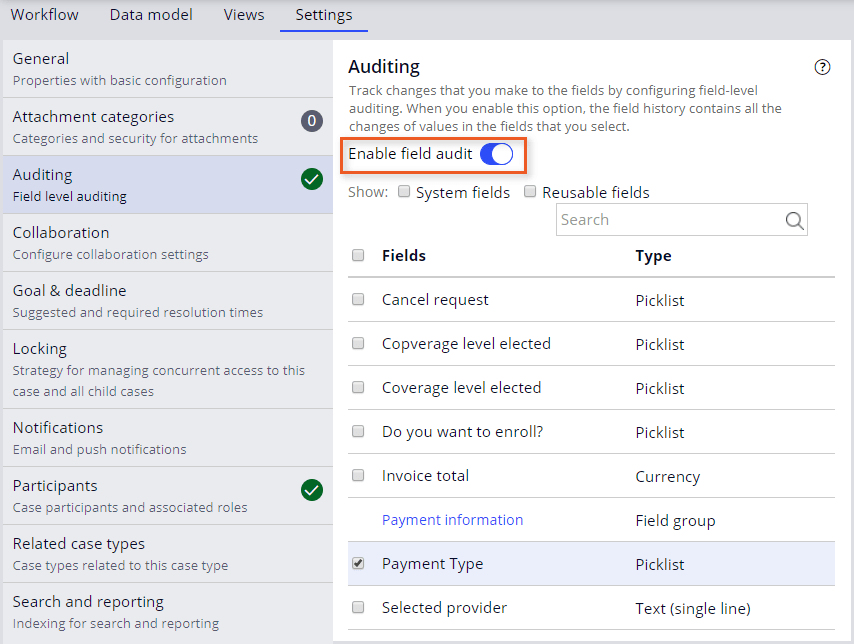
Field level auditing in Pega involves a systematic approach to examining and evaluating individual fields within a data record. This process ensures the accuracy, completeness, and validity of the data stored in the system.
The methods and procedures used for field level auditing in Pega include:
Data Validation
- Data validation rules are established to ensure that the data entered into a field meets specific criteria, such as data type, format, range, and uniqueness.
- These rules are applied during data entry and can prevent invalid data from being stored in the system.
Data Profiling
- Data profiling involves analyzing the data in a field to identify patterns, trends, and anomalies.
- This analysis can help to identify potential data quality issues, such as missing values, outliers, or inconsistencies.
Data Reconciliation
- Data reconciliation compares data from different sources to ensure consistency and accuracy.
- This process can help to identify and correct errors or inconsistencies in the data.
Data Lineage
- Data lineage tracks the origin and transformation of data throughout the system.
- This information can be used to identify the source of data quality issues and to ensure that data is being used consistently.
Exception Handling, Field level auditing in pega
- Exception handling procedures are established to manage data that does not meet the expected criteria.
- These procedures can include flagging the data for review, rejecting the data, or taking corrective action.
Data Collection and Analysis
Data collection and analysis are crucial steps in field level auditing in Pega. Auditors gather various types of data to assess the accuracy and completeness of business processes and identify areas for improvement.
The collected data is analyzed using a variety of techniques, including statistical analysis, data visualization, and trend analysis. This analysis helps auditors identify patterns, trends, and anomalies that may indicate potential risks or areas for improvement.
Types of Data Collected
- Transaction data:This includes data related to individual transactions, such as purchase orders, invoices, and payments.
- Master data:This includes data about entities involved in business processes, such as customers, suppliers, and employees.
- Process data:This includes data about the flow of work through business processes, such as the time it takes to complete a task or the number of errors that occur.
- System data:This includes data about the IT systems used to support business processes, such as the software versions and hardware configurations.
Data Analysis Techniques
- Statistical analysis:This involves using statistical methods to identify trends, patterns, and correlations in the collected data.
- Data visualization:This involves using charts, graphs, and other visual representations to make the data easier to understand and identify patterns.
- Trend analysis:This involves analyzing data over time to identify trends and patterns that may indicate potential risks or areas for improvement.
Examples of Data Analysis
- Auditors may use statistical analysis to identify trends in the number of errors that occur during a particular business process. This analysis can help auditors identify the root cause of the errors and develop recommendations for improvement.
- Auditors may use data visualization to create a dashboard that shows the status of key business processes in real time. This dashboard can help auditors identify potential risks and take corrective action before they become major problems.
- Auditors may use trend analysis to identify trends in the time it takes to complete a particular business process. This analysis can help auditors identify bottlenecks and develop recommendations for streamlining the process.
Reporting and Communication
Field level auditing in Pega generates various types of reports to convey the results of the audit. These reports provide insights into the effectiveness of the business processes, compliance adherence, and areas for improvement.
Field level auditing in Pega is a crucial process that ensures data integrity and compliance. To enhance your understanding, consider exploring the letrs unit 1 4 post test , which provides valuable insights into field-level auditing concepts. By understanding these principles, you can effectively conduct field level auditing in Pega, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of your data.
Methods of Communication
The results of field level auditing are communicated to stakeholders through various methods, including:
- Verbal Communication:Presenting findings and recommendations in meetings or briefings.
- Written Reports:Comprehensive reports that document the audit process, findings, and recommendations.
- Dashboards and Visualizations:Interactive dashboards and visualizations that provide real-time insights into the audit results.
- Follow-up Actions:Assigning specific actions and responsibilities to address the audit findings.
Best Practices
Field level auditing in Pega demands a strategic approach, and adhering to best practices ensures its effectiveness. These practices encompass planning, documentation, and continuous improvement, each playing a vital role in enhancing the quality and efficiency of audits.
Planning
- Define clear audit objectives and scope.
- Identify key stakeholders and involve them in the planning process.
- Establish a realistic timeline and allocate adequate resources.
- Develop a comprehensive audit plan outlining the methodology, data collection techniques, and reporting format.
Documentation
- Maintain detailed audit records, including audit plans, checklists, and findings.
- Document all interactions with stakeholders, including interviews, observations, and feedback.
- Keep a record of all supporting evidence gathered during the audit.
Continuous Improvement
- Regularly review and evaluate audit processes to identify areas for improvement.
- Seek feedback from stakeholders and incorporate it into future audits.
- Stay updated on industry best practices and incorporate new techniques and technologies into audits.
By implementing these best practices, organizations can ensure that field level audits in Pega are conducted efficiently, effectively, and contribute to ongoing process improvement.
Key Questions Answered: Field Level Auditing In Pega
What is the primary objective of field level auditing in Pega?
To evaluate the accuracy, completeness, and validity of data at the field level, ensuring data integrity and compliance with business rules.
How does field level auditing contribute to operational efficiency?
By identifying data errors and inconsistencies, field level auditing helps organizations streamline processes, reduce rework, and enhance overall performance.
What are some best practices for conducting field level auditing in Pega?
Thorough planning, meticulous documentation, continuous monitoring, and regular training are crucial for ensuring the effectiveness and efficiency of field level auditing.